Websocket
Guide to websocket communications with the Ardexa API
Getting started
The Ardexa API uses socket.io (https://socket.io/) for websocket requests. There are client libraries available for a variety of programming languages. The examples listed here will use NodeJS.
To get started, we will issue a simple REMOTE SHELL request. You will need:
An API token with the Control Devices privilege
For testing, you can simply use your current session token: (Your name) -> My Profile -> Version -> Copy to clipboard
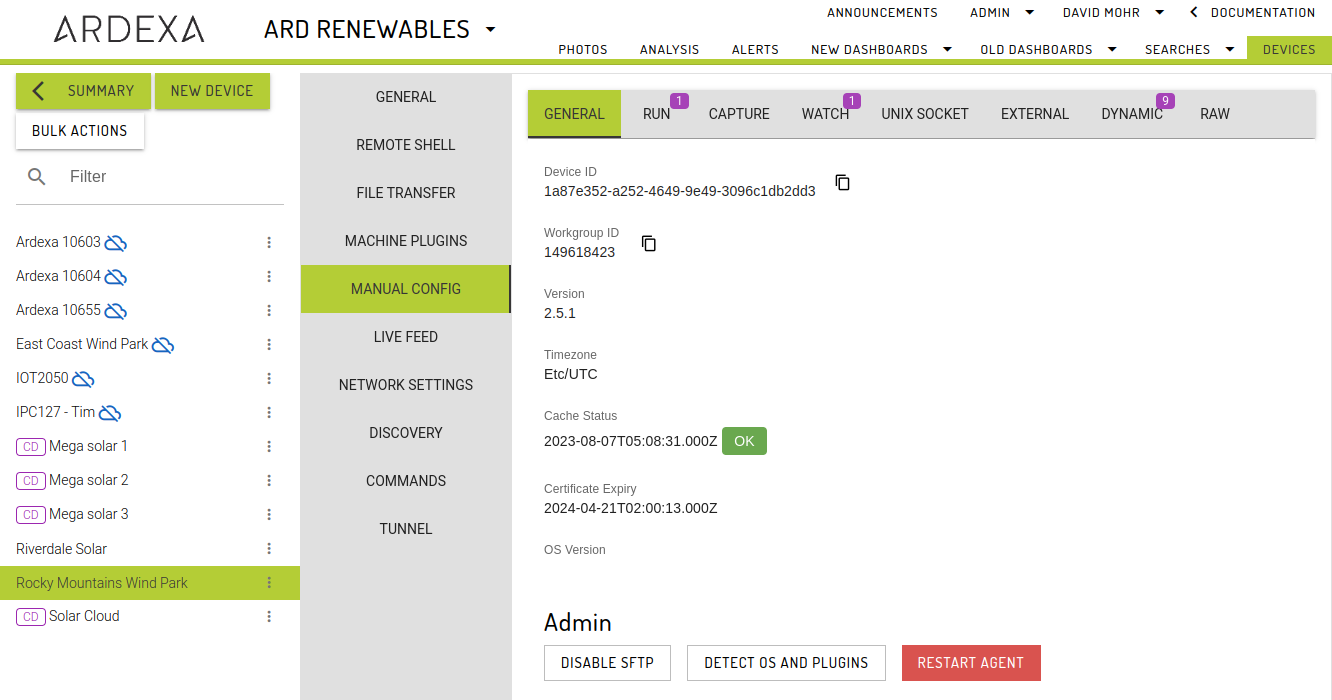
The workgroup ID and device ID of the device
These can be found under Manual Config -> General on the Devices page for the target device
Connect and authenticate
Here is an example connect function:
All operations using socket.io are event driven, so in this example we have wrapped the connection events in a Promise to make things a little easier. The important parts to notice are:
The API token is read from an environment variable called
TOKENThe cloud is
app.ardexa.com. Please update this to match your cloud URL.The
workgroupIdis passed in at connection time. You must use a separate connection for each workgroupThe websocket will emit
connectwhen successfully connected, orconnect_errorif there was a problem
Now that we're connected, we can issue a REMOTE SHELL by emitting (sending) the correct event type and listening for the responses
device:cmdis emitted with the following parametersdeviceId: the ID of the target devicecmd: the command we want to run on that devicerequestId: optional. Will be returned in any subsequent replies. Useful for matching requset and response objects if you are running many concurrent requests
device:cmd:rpcis received first. This confirms that the API has received the request and it has been successfully processed. If there are errors, such as a permission problem, they will be delivered here and there will be noreply. Successful requests will be assigned acorrelationIdwhich can be used to match the reply/replies to the initial requestdevice:cmd:replyis received once the request has been fully processed by the edge device. Fordevice:cmd, this includes the output of the command (stdout and stderr) as well as the return code.
Here is a sample of the output when the script is run from the command line:
Emitted events
device:stateChange
Sent when a device's online state changes (online/offline). Contains the cn (Common name), vhost (aka workgroup ID) and the latest online status
device:new
Sent when a new device is created. Contains the id (aka Device ID), the cn and it's online status (which is always false)
device:metaChange
Sent when there is a change to the agent configuration. Contains the device ID as the id property. The workgroup ID is the one used to connect the current socket.
RPC events
Live data feed
device:feed
Get a live feed of data directly from the broker. The deviceId, table and source are mandatory. For CSV scenarios you can optionally include a specific field to only stream a single value (the default is to stream an array of values)
The device:feed:rpc will include a feedId:
The value prop will contain the value(s) requested:
device:feed:stop
Will stop an existing feed. Simply pass in the feedId received in the :rpc response
device:feed:stopAll
Takes no arguments, will stop all feeds associated with the current socket connection.
Agent configuration
device:testConfig
Send a config object (JSON) to the specified device ID for testing and validation. Since the destination format is YAML, but the request is using JSON, the API will pre-process the request to look for "anchors" in the config, specifically in the fields property. In the example below, example_fields is used as an anchor by the tail scenario.
As the request is fairly determinate in terms of time taken, there is only a single :rpc response indicating success:
Or failure:
device:applyConfig
Just like device:testConfig, except the configuration will be saved and the agent will be restarted
device:applyYamlConfig
Just like device:applyConfig, except the configuration is a String instead of an Object, and the string must be a YAML document.
Other
device:refreshMeta
Dynamically mapped scenarios (read: anything logged to /opt/ardexa/logs), can occasionally get out of sync with the cloud. To force a re-read and re-sync event, use this RPC request
Will always succeed
Will be followed by a device:stateChange as the agent is restarted, and a device:metaChange as the metadata is re-synced
device:doUpgrade
Upgade the agent to the latest version
Will emit a series of device:doUpgrade:reply events at each step of the process
The final message in a successful series will set complete: true
If there is an error, it will be reported and no further replies will be forthcoming
device:sendArdexactl
Send a cooy of the ardexactl control script to the target device. This normally happens automatically if the script is required, e.g. device:doUpgrade, but there are situations where that's not the case, such as agent API logins.
And the device:sendArdexactl:rpc response
device:sendArdpkg
Send a cooy of the ardpkg plugin management app to the target device. This normally happens automatically if the script is required, e.g. installing a plugin. This call can also be used to upgrade ardpkg to the latest version
And the device:sendArdpkg:rpc response
Last updated