Audit Logs
Tracking your workgroup usage & events
About Audit Logs
Audit logs are provided to you as a means to track key events and user usage generated within your workgroup in the Ardexa Web App . Example events captured include by whom and when; a file is sent to your device, or a device was moved to another workgroup, when a user logged-in, or when a device was renamed.
A detailed breakdown of audited events is provided below.
NOTE: Records captured in the audit_logs table are kept indefinitely.
Who can access and view Audit Logs?
Access to view this data is dependent on your workgroup and your role within that workgroup:
User role(s) of type:
ownerare able view theaudit_logstable to conduct searchesAnyone with the
read audit logspermission.
All other role types do not have access to this data.
Where can I see the Audit Logs in the Ardexa Web App?
Under the [SEARCHES] tab, select the audit_logs table to begin building your search against this data.
Search Criteria for Common Searches
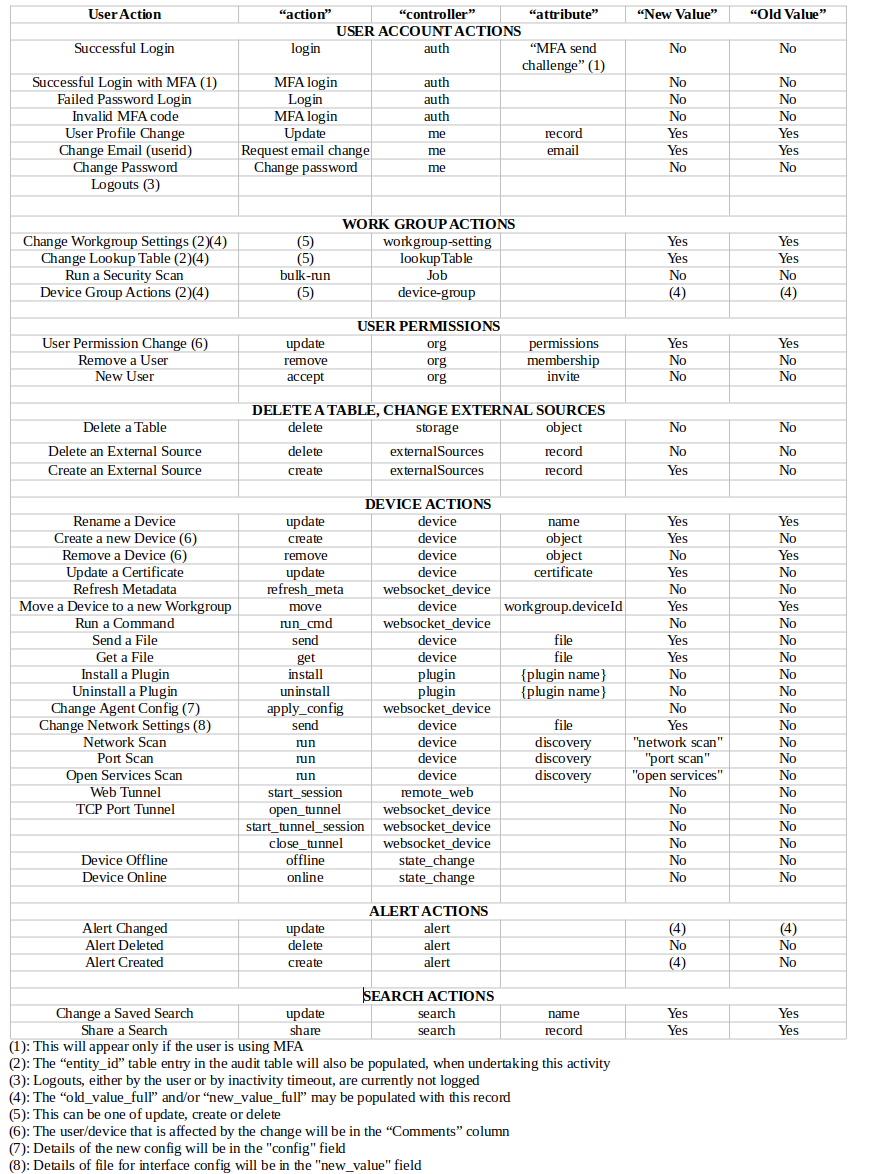
There are a number of fields associated with the audit trail, as discussed in the sections below. This image shows the common user actions that are logged, and how to search for them in the audit traill. The "action", "controller", "attribute", "new value" and "old value" refer to the fields in the audit trial. Please be aware that all the actions below have the "user_id" field populated by the user that made the change. Also, the "status" field will indicate the success or failure of the command.
How to read and understand your audit_logs searches
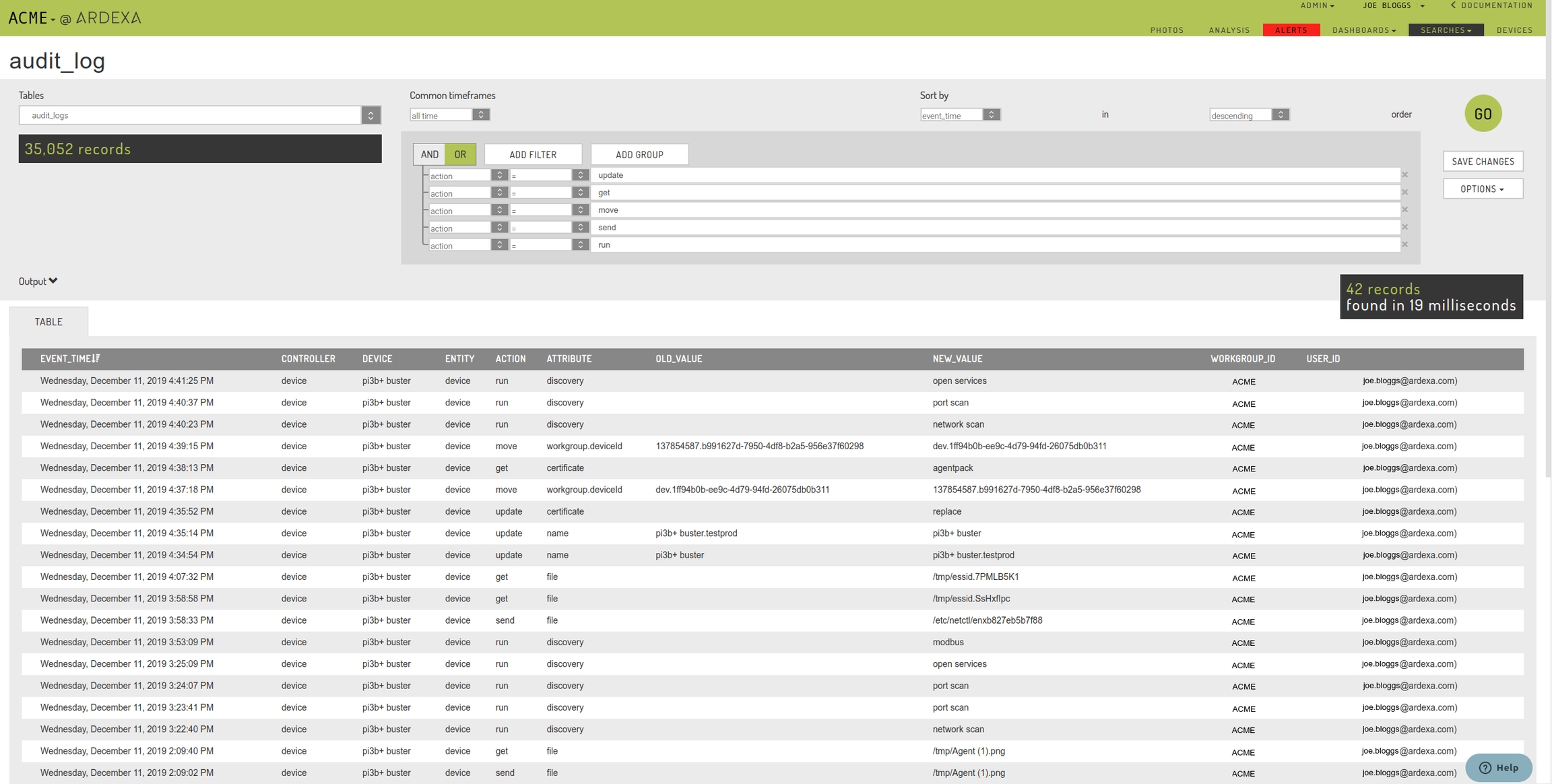
The audit_logs table works like any other search. You can build filters and show the columns relevant to your needs. To understand how you might go about reading this data, provided here, are the most important fields and their description:
Field | Always? | Description |
EVENT_TIME | Y | When the event was recorded. |
CONTROLLER | Y | The component inside the Ardexa Web App that recorded and applied the event against the |
DEVICE | N | The device that the event was related, if the event was actually related to a device. |
ENTITY | Y | The unit or something that was worked upon. Examples might be: |
ACTION | Y | The simple description of the event. Examples might be:
|
ATTRIBUTE | N | A simple description of the attribute that was affected by the action |
OLD_VALUE | N | If a prior value of the attribute is relevant and available for the action being applied then it will be captured here. |
NEW_VALUE | N | Specifics for the audit event are captured here. For example: new attribute values, files names, descriptors of the event |
STATUS | N | Reports if the attempted action was |
WORKGROUP_ID | Y | The user's workgroup that the was active when the user triggered the event. |
USER_ID | Y | The user's details that triggered the event. |
Can the audit_log Table be Deleted?
No.
The audit_log table is among a number of system tables that can never be deleted.
Any attempt to delete a table or an index, the audit_log table itself included, whether it succeeds or fails, is recorded as an entry in the audit_log table. This can be viewed through your searches on the audit_log table.
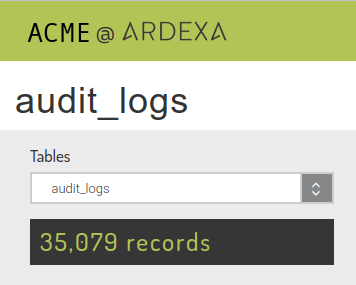
An example audit_logs concise search
Last updated